DIBMA 10, HEPES
Order number: 18001
Description
With diisobutylene-maleic acid (DIBMA) you can directly extract membrane proteins from cells without an intermediate step of detergent solubilization, like with SDS that would usually interfere with the proteins function. Another advantage of DIBMA as a tool for protein solubilization is the lack of an absorbance maxima at 280 nm. In comparison to SMAs, this would usually interfere with protein quantification, as aromatic amino acids absorb at the same spectrum. PureCube DIBMA is lyophilized from two different buffer solutions (HEPES or TRIS) to ensure a stable pH of 7.5, which is ideal for most protein solubilizations. A good publication to read up even more details about DIBMA is Oluwole et al. 2017.
| Features | |
|---|---|
| Usage | Protein solubilization |
| Formula Weight | 10,000 g/mol |
| pH | 7.5 in buffer |
| dn/dc | 1.35 M-1 |
| Solubility | > 10 % in H2O |
| Absorbance at 280 nm | < 0.3 (1 % solution) |
| Mg2+ Tolerance | Dependend on DIBMA product Increased with less charged DIBMAs |
| Ca2+ Tolerance | Dependend on DIBMA product Increased with less charged DIBMAs |
| Shipping Temperature | ambient temperature |
| Storage of lyophilized copolymer | -20°C for several years |
| Storage of dissolved copolymer | 2-8°C for several days |
Citations
| Stabilized Protein | Year | Author |
|---|---|---|
| ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter | 2023 | Dimitrova V.A., Song S., Karagiaridi A., Marand A., Pinkett H.W. |
| Env-protein of HIV | 2023 | Zhou R., Zhang S., Nguyen H.T., Ding H., Gaffney A., Kappes J.C., Smith III. A.B.S, Sodroski J.G. |
Lab Results
For the longest time, the science behind membrane proteins relied on detergents for both solubilization and stabilization. However, detergents such as DDM or LMNG come with a set of problems. A time-consuming screening process for the correct detergent and the constant need to add it to all buffers can be avoided. But this applies to all synthetic nanodiscs.
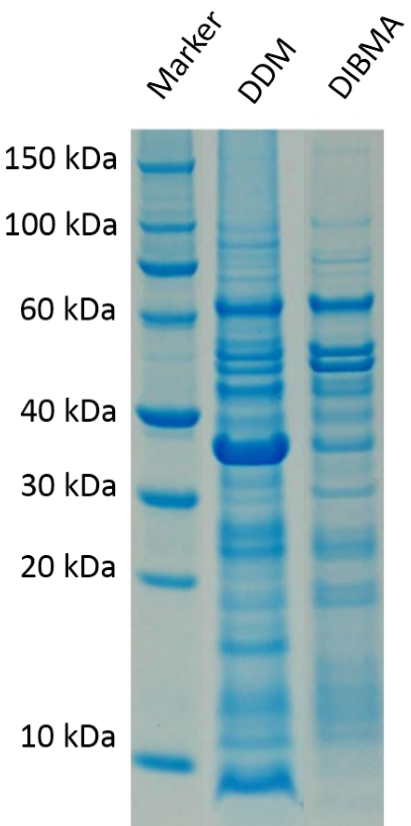
Figure 1 shows the amount of membrane protein of interest that was stabilized by a DIBMALP in comparison to a construct using the detergent DDM. As it can clearly be seen DDM has way fewer specific bands at the desired kDA values of around 40-60 kDa.
Figure 1 shows the amount of membrane protein of interest that was stabilized by a DIBMALP in comparison to a construct using the detergent DDM. As it can clearly be seen DDM has way fewer specific bands at the desired kDA values of around 40-60 kDa.
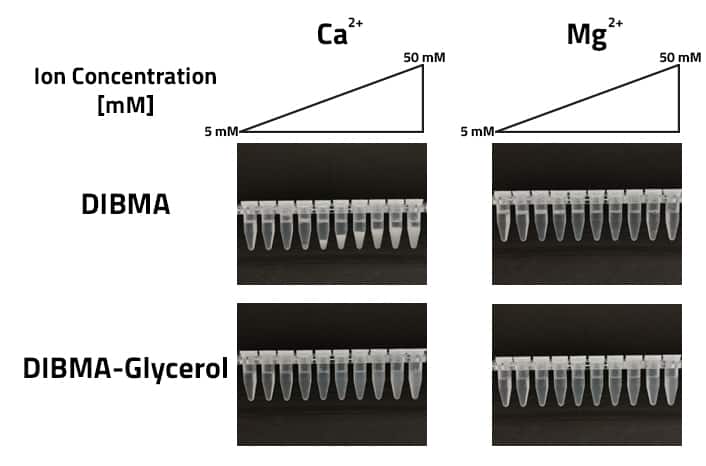
An alternative to traditional DIBMAs and their sensitivity to the presence of ions inside a buffer, are our modified DIBMAs with added Glucosamine or amino-functionalized diol.
As figure 2 indicates, the increased tolerance of Ca2+ is necessary. Normally DIBMA starts to precipitate in Ca2+ holding buffers at concentrations of around 25 mM. Using DIBMA-Glycerol this tolerance increases to 50 mM. There is no precipitate visible at the bottom of the tube. In comparison, normal DIBMA shows a visible precipitate at 25 mM. In terms of Mg2+ tolerance traditional DIBMA and the Glycerol-DIBMA both show a high tolerance above 50 mM.
Video
Watch our video on how nanodiscs can help you to overcome one of the most difficult challenges in protein sciences.
FAQ
Is DIBMA from Cube Biotech ready to use?
Yes, our DIBMA is ready to use. You can start directly with the solubilization. Read our protocol for more information.
Which pH is suitable for DIBMA?
For DIBMA a pH of 7.5 is recommended. DIBMA does not solubilize if the pH is smaller than 6.5.
Which concentrations of DIBMA should I use for my protein?
In general, we advise you to add 2,5 % DIBMA to your solution. But the optimal conditions have to be screened by yourself (Fig. 4).
I used DIBMA for protein solubilization and a white precipitate appeared - what happened?
Your DIBMA precipitated. You should check your pH and ensure that your pH never drops down to 6.5.



