Custom Beads
.jpg)
What are Custom Beads for?
If commonly used protein tags do not work for your protein purification, you do not have to despair. The solution to your problem is the use of protein specific ligands instead of artificially added tags. These ligands are the key for 100% specific purification of the desired protein. This way purification from native tissue as well as from denaturing enviroments are possible.
Cube Biotech has performed many custom resin & beads projects and you can make this experience work for you!
One of our numerous successful examples (Table 1) is the coupling of the cobra venom neurotoxin-3 onto agarose resin. This leads to a high-yield and 100% specific purification of the Acetylcholine receptor (AChR) Torpedo california, which the venom binds to naturally. In fact, this project was so successful that we added AChR to our standard product catalogue!
Cube Biotech has performed many custom resin & beads projects and you can make this experience work for you!
One of our numerous successful examples (Table 1) is the coupling of the cobra venom neurotoxin-3 onto agarose resin. This leads to a high-yield and 100% specific purification of the Acetylcholine receptor (AChR) Torpedo california, which the venom binds to naturally. In fact, this project was so successful that we added AChR to our standard product catalogue!
Applications for protein-specific purification matrices
While tag-based affinity matrices afford a standardized and consistent method to purify proteins, the versatility of affinity matrices is only first apparent when coupled to molecules that interact directly with the protein of interest. Loading a matrix with protein-specific ligands, agonists, antibodies, peptides, small proteins, or other molecules enables new experimental applications.Cube Biotech produces tailor-made affinity resins or magnetic beads. You determine the coupled molecule, its coupling orientation, and whether it should be bound with a cross-linker or a spacer. We can advise you on the most suitable coupling strategy for your application. For example, we offer a choice of spacer lengths and special linkers that can be cleaved under reducing conditions or by UV light. You can even send a publication for us to duplicate. We develop pilot synthesis reactions to your specifications and work with you to evaluate the utility and quality of the resulting pilot matrices. We then produce the best performing matrix in the quantities needed—from a few milliliters to bulk volumes.
The possibilities are endless; here are just a few examples of what you can do:
Purify proteins without an affinity tag: in the case that affinity tags interfere with the structure and function of the target protein, or that eluents or compounds that leach from resins have toxic effects, a target protein can be captured on an affinity matrix loaded with a ligand known to specifically bind the protein.
Select only proteins in native, active state: taking advantage of the specificity of protein-ligand interactions, a matrix can be loaded with a ligand that does not interact with misfolded or unfolded proteins.
Purify proteins in a particular conformation: for structural analyses, a matrix is loaded with molecules that bind a protein only in a particular functional conformation or oligomeric state thereby separating alternative conformations.
Conduct functional studies with natural, synthetic, or protein ligands: determine binding affinity and other functional parameters of a target protein by exposing it to any ligand—natural, synthetic, protein, antibody—coupled to an affinity matrix.
Examine protein-agonist interaction: a matrix loaded with a synthetic agonist is a prime reaction surface to study binding and response of a target protein. The density of the agonist on the matrix can be determined and adjusted using spacer molecules. Additionally, the functional group used to couple agonist and matrix can be defined so the orientation of the molecule maximizes interaction with the protein.
Avoid alteration to the target protein due to sub-optimal elution conditions: elution conditions may interfere with important features of a protein. Crosslinker molecules that are chemically or light-cleavable offer an alternative method to bring a protein off the resin. The eluted protein still binds the ligand making it suitable for downstream applications such as co-crystallization experiments.
Whatever your needs or ideas, we would be happy to discuss and assist you in developing your project. If required, all information regarding a commissioned project is kept strictly confidential and your protein-specific matrix can be produced on an exclusive basis.
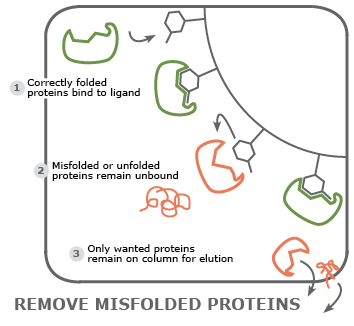
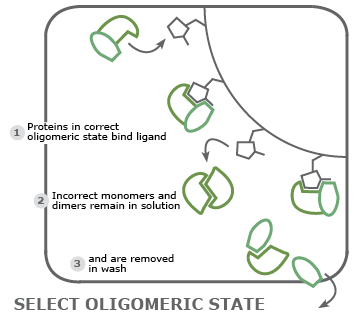
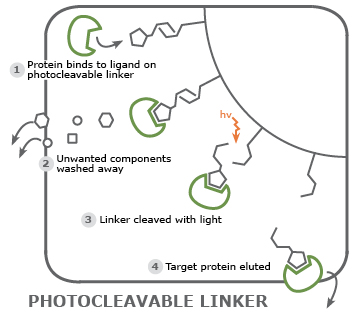
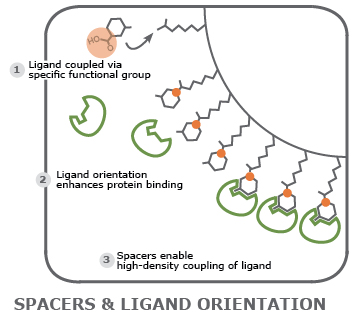
Examples for Custom Beads by Cube Biotech

The applications of customized resins/beads extent to numerous possibilities of proteomics and sometimes beyond. Figure 1 shows our favourite example of custom beads, while more is listed in table 1.
Table 1: Customized resins from Cube Biotech
| Base Materials | ||
|---|---|---|
| Magnetic Agarose | Diameters: 30 µm, 90 µm 400 µm, 800 µm MWCO: from 4 MD up to 20 MD |
|
| Agarose | Diameters: 40 µm, 100 µm, 400 µm, 800 µm MWCO: from 150 kD up to 10 MD |
|
| Hollow agarose particles | - | |
| Hydrogels | e.g. Toyopearls for ligand immobilization | |
| Organic Polymers | e.g. Dynabeads, Seradyn MagBeads,Luminex particles | |
| Submicron and Nanoparticles | 500 nm-sized polymers coupling of antibodies onto carboxylated nanoparticles |
|
| Surfaces | e.g. coupling of amino-functionalized ligands onto Pierce amine-binding strip plates | |
| Spherical Cellulose/Carbohydrates | Diameters: 50 and 100 µm MWCO 5 kD upto 50 kD |
|
| Coupled Molecules | ||
| Ligands | Alprenolol, Desipramin, Fluoxetedin, Serotonin, Heparin, Insulin, Biotin, Xanthin, Lumochrom, Carnitin, Riboflavin, 2,3-GMP, cAMP, Cyclocitral, AZD 8055, Methylthioadenosin, Nicotinic acid, Pipecolinic acid, Actinonin | |
| Carbon hydrates | - | |
| Amino acids | protected and non-protected | |
| Peptides | Exendin, Endomorphin | |
| Antibodies | Rho1D4, FLAG, different others | |
| Proteins | - | |
| Klick reagents | Tetrazine, Azide | |
| Fluorophors and colorants | - | |
| Cholesterol derivatives | cholesterol hemisuccinate, ketocholesterol | |
| Binding Chemistries | ||
| Many different coupling chemistries | amide chemistry, epoxide/amine, maleimide/thiol, reductive amination, thiol/alkene | |
| Spacer | from C0 via C6, C11 up to C45 | |
| Amino acids | protected and non-protected | |
| Peptides | - | |
| Antibodies | Rho1D4, FLAG, different others | |
| Proteins | - | |
| Klick reagents | Tetrazine, Azide | |
| Fluorophors and colorants | - | |
| Applications | ||
| Protein-specific purification and pulldown | ||
| (Membrane) protein purification | ||
| Purification of carbohydrates | ||
| Immobilization of DNA/RNA, oligonucleotides | ||
| Electron transfer reagents in fuel cells | ||
Custom Bead Creation
Three decisions have to be made for the creation of a customized bead product by Cube Biotech. Table 2 leads you through these decision process and gives you some guidance.
Table 2: Choose matrix, format and ligand and we will create your custom resin.
| 1. Choose a matrix | |
|---|---|
| The first question that needs to be answered is "Agarose Resin or MagBeads?" This is mostly a question on your personal preference to one of the methods. Do you favor batch spin columns and drip columns or do you prefer magnetic bead based methods? | |
| Agarose Resin | Magnetic Beads |
 |
 |
|
Our agarose resin is very homogeneous in size, yielding a high degree of reproducibility between individual purification runs. The cross-linked agarose is physically stable and highly porous for optimal protein interaction.
|
Our ferrimagnetic agarose beads are produced in house and are ideal for extracting proteins from diluted samples or for pull-down experiments.
|
| 2. Choose a format | |
| The second decision is regarding the format in which the resin or MagBeads should be created. For MagBeads bulk deliveries are preferred, while in regards to agarose resin you can choose between bulk resin and pre-packed resin in FPLC Columns. | |
| Bulk | FPLC Columns |
|
Resins are prepacked in high-quality columns of 1 or 5 mL bed volume, ready to be used on most FPLC workstations. |
| 3. Choose a tag or ligand | |
| The third and probably the most important question surrounds the ligand that should be coupled to the beads. Have a look at table 1 to see what we already managed to accomplish. | |
| Nonetheless you should have a look on our standard protein purification products, maybe one of our existing beads can help you out. | |
| Cube Biotech protein purification products | |
| Polyhistidine / His-tag The workhorse of affinity tags. This His-tag is short and can be added to both termini of a protein. The tag is designed for highest protein yields. |
Our His affinity agarose resins and MagBeads by Cube Biotech for highest protein yields.
|
| Glutathione Affinity / GST-tag A 26 kDA large affinity tag that consists of the protein Glutathione-S-transferase. Preferably added to the N-Terminus |
Our GST-tag affinity agarose resins and MagBeads by Cube Biotech for a great balance between protein yield and purification specificity. |
| Streptactin / Strep-tag® An eight amino acid long affinity tag that provides high levels of protein purity |
Our Strep-tag® affinity products by Cube Biotech as a smaller alternative to the GST-tag while having similar purification properties.
|
| Rho1D4-tag A nine amino acid long affinity tag that provides our highest levels of protein purity and membrane protein purification |
Our Rho1D4-tag affinity products by Cube Biotech for membrane protein purification.
|
| Hydrophobic Interaction Resins A reasonable option for protein purification using hydrophobic interactions between protein and agarose bead. |
Our HIC products by Cube Biotech protein purification without the use of affinity tags.
|
| Your ligand
Protein-specific ligands bind targets in particular oligomeric states, conformations or orientations, enabling specialized applications.
|
PureCube Tailor-made Resins
Our custom resins are produced within a couple weeks after ordering and/or consultation with our chemistry experts. You lay out the matrix parameters (e.g., ligands, linker, spacer, etc.), and we produce it in the quantities you need.
|


