DIBMA 6 Fluorescein
Order number: 18762
Description
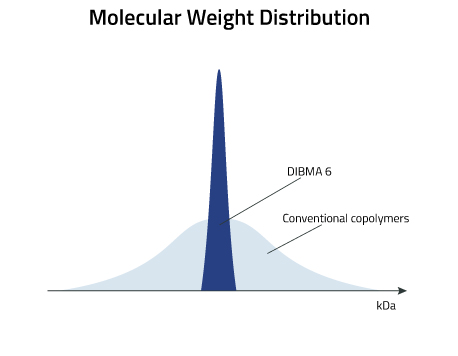
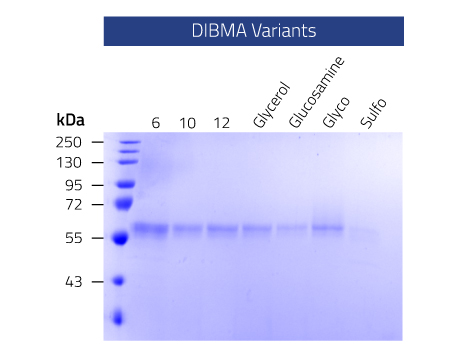
The new DIBMA 6 is not only smaller than its predecessors (DIBMA 10 and DIBMA 12) but together with Sulfo-DIBMA belongs to a new generation of DIBMA’s which are RAFT polymerized. This achieves a reduction in both monomer size and lower polydispersity, meaning that if you need your copolymers to all have a similar size this is the copolymer to choose.
Suitable applications for fluorescent copolymers:
If you’re interested in having this functionalization applied to a different copolymer backbone, get in touch with us and we’ll get that project running for you: Contact us
DIBMA 6 Fluorescein
This first-of-its-kind, functionalized version of our classic DIBMA 6 is fluorescently labeled with fluorescein. This means a pH-dependent fluorescent excitation at ~485 nm and emission maximum at ~510 nm.Suitable applications for fluorescent copolymers:
- Detection
- Localization (Visualization via fluorescent microscopy)
- etc.
If you’re interested in having this functionalization applied to a different copolymer backbone, get in touch with us and we’ll get that project running for you: Contact us
Datasheets
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| State | Lyophilized Powder, to be solved with water |
| Full Name | Diisobutylene Maleic Acid Fluorescein in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5 |
| Buffer | HEPES |
| pH after solving | 7.5 |
| pH Stability of Copolymer | 5.0-10 |
| Absorbance at 280nm | Yes |
| Molecular Weight | 6 kDA |
| Ca2+ tolerance | 30 mM |
| Mg2+ tolerance | 40 mM |
| Solubility | > 10% (H2O) |
| Polymerization Type | RAFT |
| λAbs | ~485 nm |
| λEm | ~514 nm |
| Shipping Temperature | Ambient Temparature |
| Storage of lyophilized copolymer | -20°C for several years |
| Storage of dissolved copolymer | 2-8°C for several days |
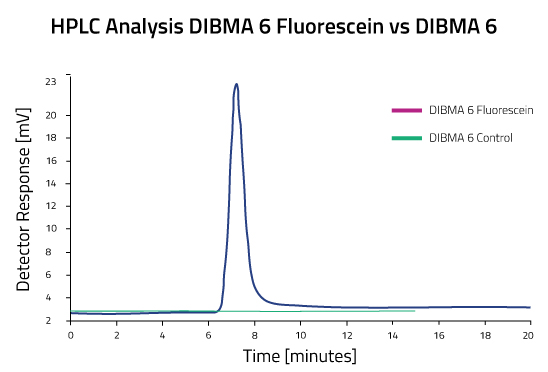
Lab Results
Disclaimer
Patent Pending
Our products are intended for molecular applications. These products are not intended for diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a disease.
Our products are intended for molecular applications. These products are not intended for diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a disease.