Sulfo-Cubipol Biotin
Order number: 19742
Description
Welcome the new addition to our NativeMP™ Platform: The Cubipol Series.
The proprietary Cubipol backbone, developed in-house, condenses the positive effects of previously available backbones like SMA, DIBMA, and UltrasoluteTM Amphipol. This new development delivers a new multimodal copolymer backbone, making the Cubipol series the first commercially available next-generation copolymer with 4 available off-the-shelf modified variants.
It joins the Next Generation Copolymers AASTY and Ultrasolute™ Amphipol, making solubilization and stabilization of membrane proteins a simpler and more effective endeavor than ever before.
The low charged, zwitterionic copolymer variation resembles softer surfactants with a high resistance to extreme pH values, ionic strength and divalent ion concentrations (details in the table below). It belongs to the Cubipol class with low charge, which allows for the uninterrupted study of charge-sensitive interactions between membrane proteins and lipids.
This functionalized copolymer is particularly suited for downstream applications that require copolymer stabilization without affecting the protein. These include drug screening, high-throughput processes and assay development.
The proprietary Cubipol backbone, developed in-house, condenses the positive effects of previously available backbones like SMA, DIBMA, and UltrasoluteTM Amphipol. This new development delivers a new multimodal copolymer backbone, making the Cubipol series the first commercially available next-generation copolymer with 4 available off-the-shelf modified variants.
It joins the Next Generation Copolymers AASTY and Ultrasolute™ Amphipol, making solubilization and stabilization of membrane proteins a simpler and more effective endeavor than ever before.
Sulfo-Cubipol Biotin
The low charged, zwitterionic copolymer variation resembles softer surfactants with a high resistance to extreme pH values, ionic strength and divalent ion concentrations (details in the table below). It belongs to the Cubipol class with low charge, which allows for the uninterrupted study of charge-sensitive interactions between membrane proteins and lipids.
This functionalized copolymer is particularly suited for downstream applications that require copolymer stabilization without affecting the protein. These include drug screening, high-throughput processes and assay development.
- Immobilization via SPR, ELISA, etc.
- Sorting (FACS)
- Quantification
- Identification
- Localization (Electron Microscopy)
If you’re interested in having this functionalization applied to a different copolymer backbone, get in touch with us and we’ll get that project running for you: Contact us
Datasheets
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| State | Lyophilized Powder, to be solved with water |
| Full Name | Sulfo-Cubipol Biotin in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5 |
| Buffer | HEPES |
| pH after solving | 7.5 |
| pH Stability of Copolymer | 5.0-10 |
| Absorbance at 280nm | No |
| Molecular Weight | 14 kDA |
| Ca2+ tolerance | 40 mM |
| Mg2+ tolerance | 40 mM |
| Solubility | > 10% (H2O) |
| Polymerization Type | Free-radical |
| Shipping Temperature | Ambient Temparature |
| Storage of lyophilized copolymer | -20°C for several years |
| Storage of dissolved copolymer | 2-8°C for several days |
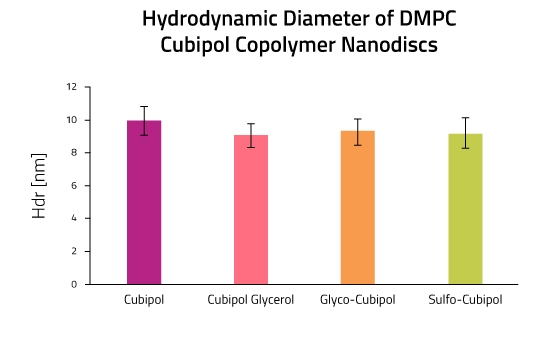
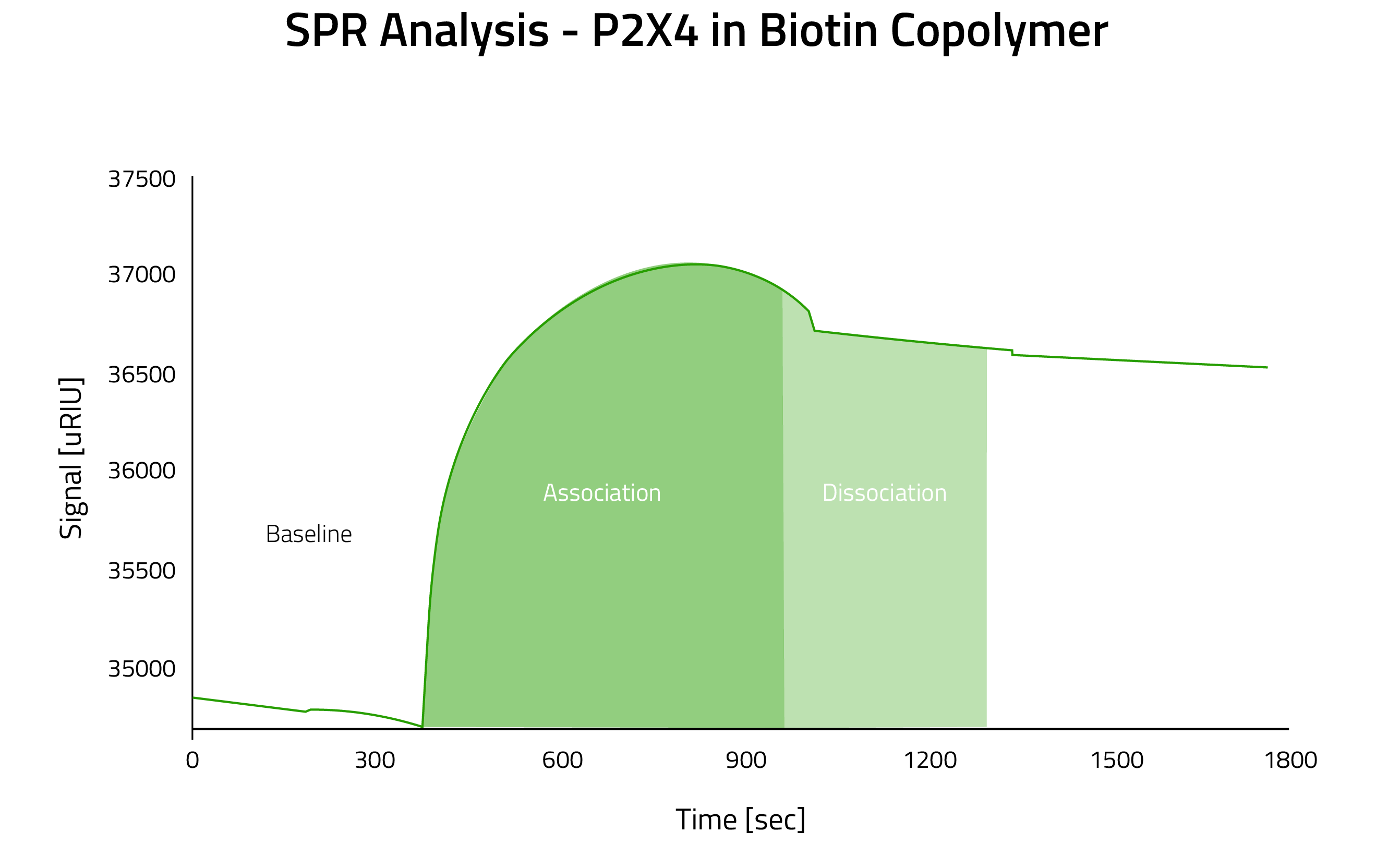
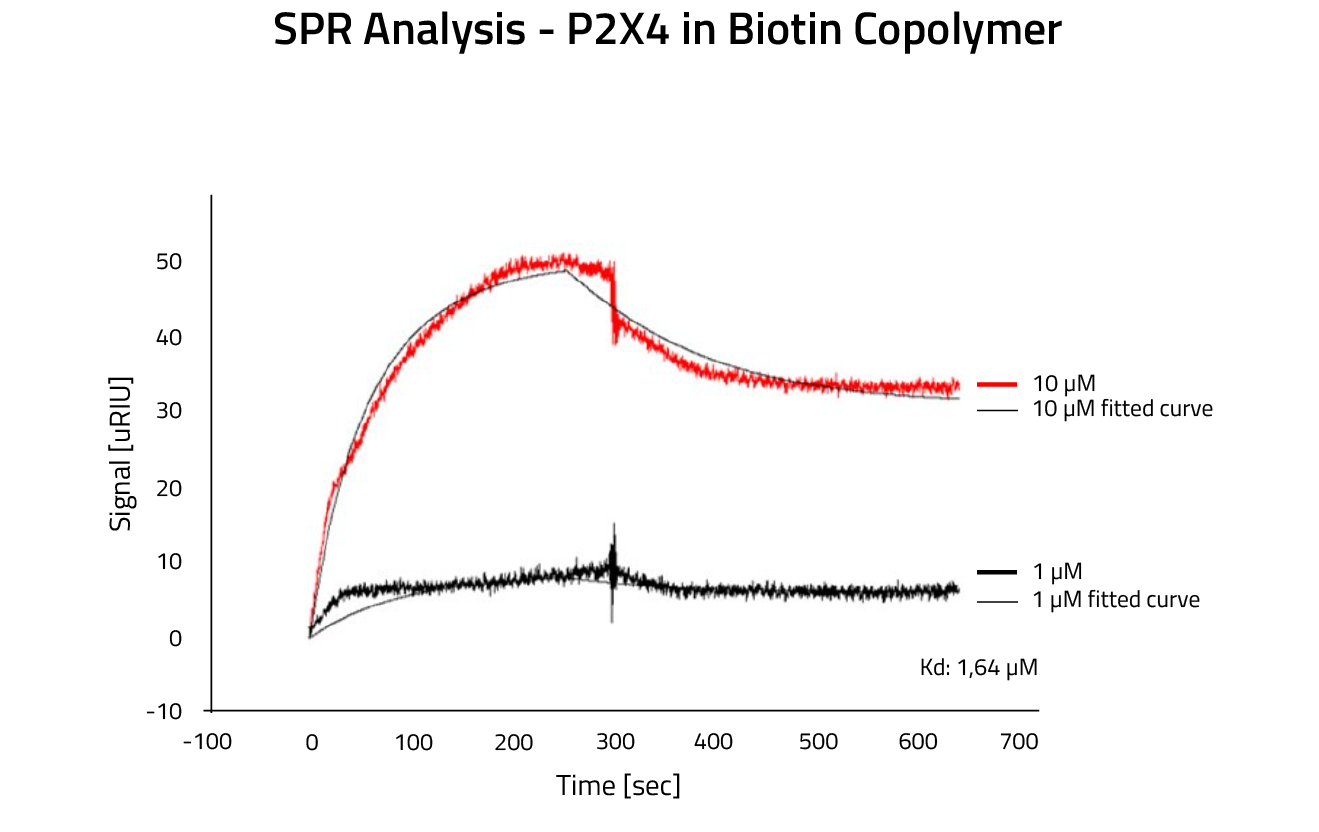
Lab Results

Disclaimer
Patent Pending
The product described above has been developed and produced by Cube Biotech GmbH. Our products are intended for molecular applications. These products are not intended for diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a disease.
The product described above has been developed and produced by Cube Biotech GmbH. Our products are intended for molecular applications. These products are not intended for diagnosis, prevention or treatment of a disease.