NativeMP™ Biotin Kit (6x1x50mg)
Order number: 19791
Description
The NativeMP™ Biotin Kit leverages a curated copolymer selection from the NativeMP™ Technology, which preserves membrane proteins in their native lipid environment without detergents. These copolymers are additionally labeled with biotin and are well suited for immobilization and downstream applications such as SPR, ELISA, FACS, and various high-throughput assays, making them ideal for drug discovery and assay development.
The copolymers are already biotinylated so that you can work with unmodified membrane proteins and avoid the extra steps necessary to label your proteins. This allows you to focus on expressing unmodified membrane proteins that can be stabilized with the biotinylated copolymers and used directly in any number of immobilization or downstream applications.
The NativeMP™ Biotin Kit offers a targeted solution for precise stabilization and solubilization without additional protein labeling.
If you’re interested in having this functionalization applied to a different copolymer, get in touch with us, and we’ll get that project running for you: Contact us
Screening is key
Each target is unique, which is why screening is just as important for biotin copolymers as it is for detergents. Our NativeMP™ Biotin Kit offers a selection of 6 biotinylated copolymers, ensuring that you’ll find the right copolymer to meet the specific needs of your target and downstream applications.If you’re interested in having this functionalization applied to a different copolymer, get in touch with us, and we’ll get that project running for you: Contact us
Datasheets
Table 1: Shared Features
All the biotin copolymers featured in this kit share the following features
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| Use | Solubilization & stabilization of membrane proteins |
| Buffer | HEPES |
| pH (upon solving in dH2O) | 7.5 |
| State upon delivery | Lyophilized powder |
| Recommended concentration for use | 1% - 5% |
| Shipping Temperature | Room temperature |
| Long-term Storage (lyophilized copolymer) | -20°C for several years |
| Short-term Storage (dissolved copolymer) | 2°C - 8°C for several days |
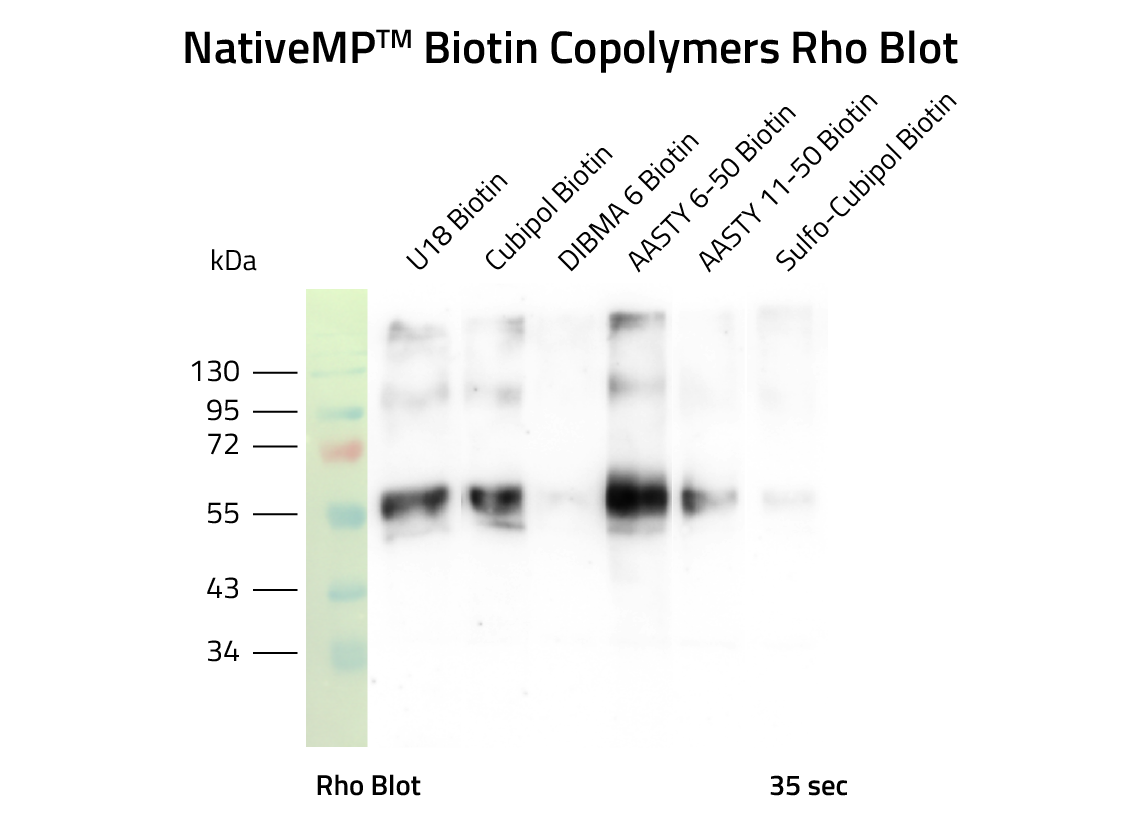
Table 2: Included Biotin Copolymers
| Feature | Ultrasolute Amphipol 18 Biotin | Cubipol Biotin | Sulfo-Cubipol Biotin | DIBMA 6 Biotin | AASTY 6-50 Biotin | AASTY 11-50 Biotin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 7,3 kDa | 7,4 kDa | 14 kDa | 6 kDa | 6 kDa | 11 kDa |
| Polymerization Type | Free-Radical | Free-Radical | Free-Radical | RAFT | RAFT | RAFT |
| Divalent Cationic Tolerance | < 25 mM | < 40 mM | < 40 mM | < 40 mM | < 6 mM | < 6 mM |
| Absorption at 280nm | No | No | No | No | Yes | Yes |
| Solubility in dH2O | <10% | < 10% | <10% | <10% | <10% | <10% |
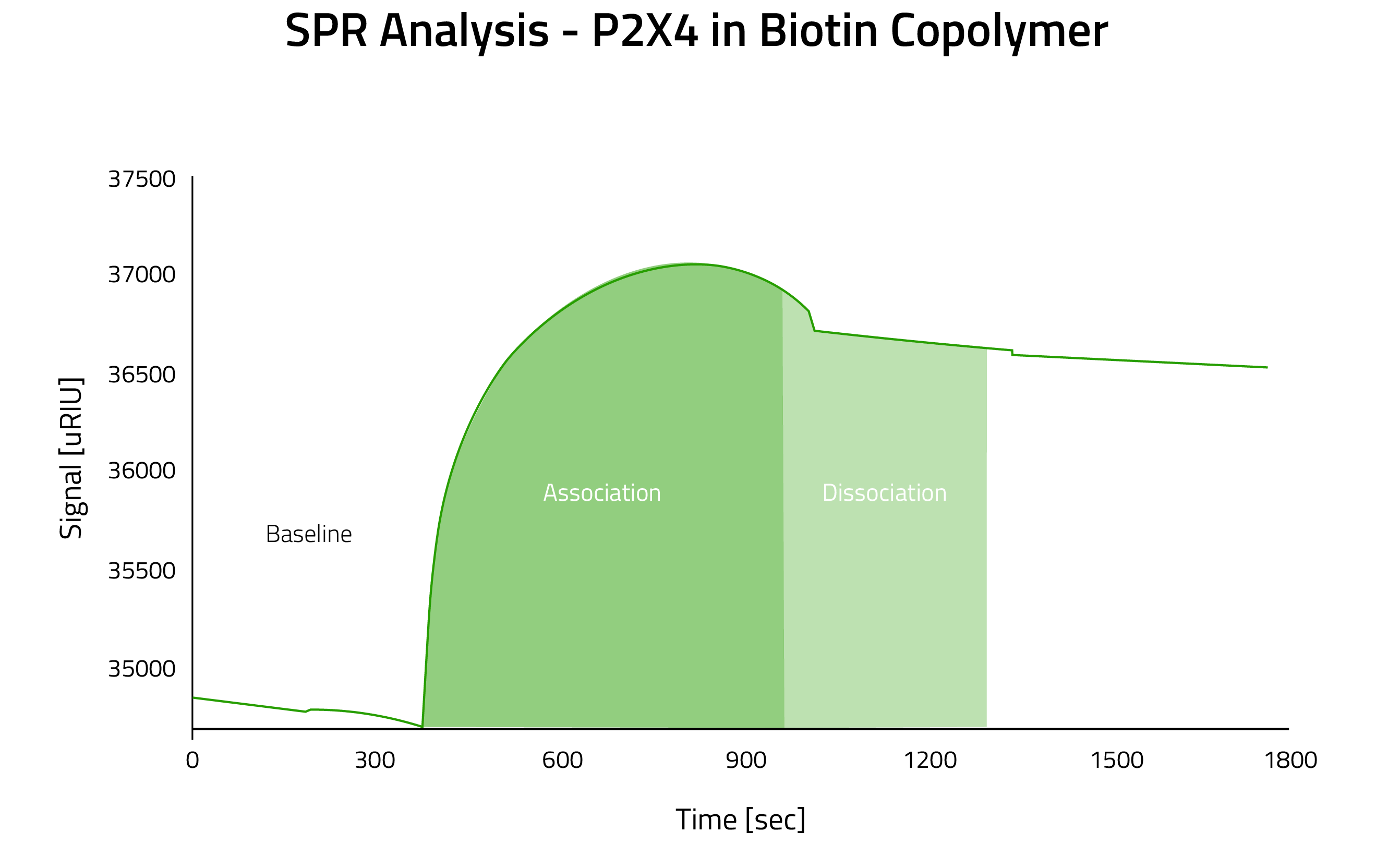
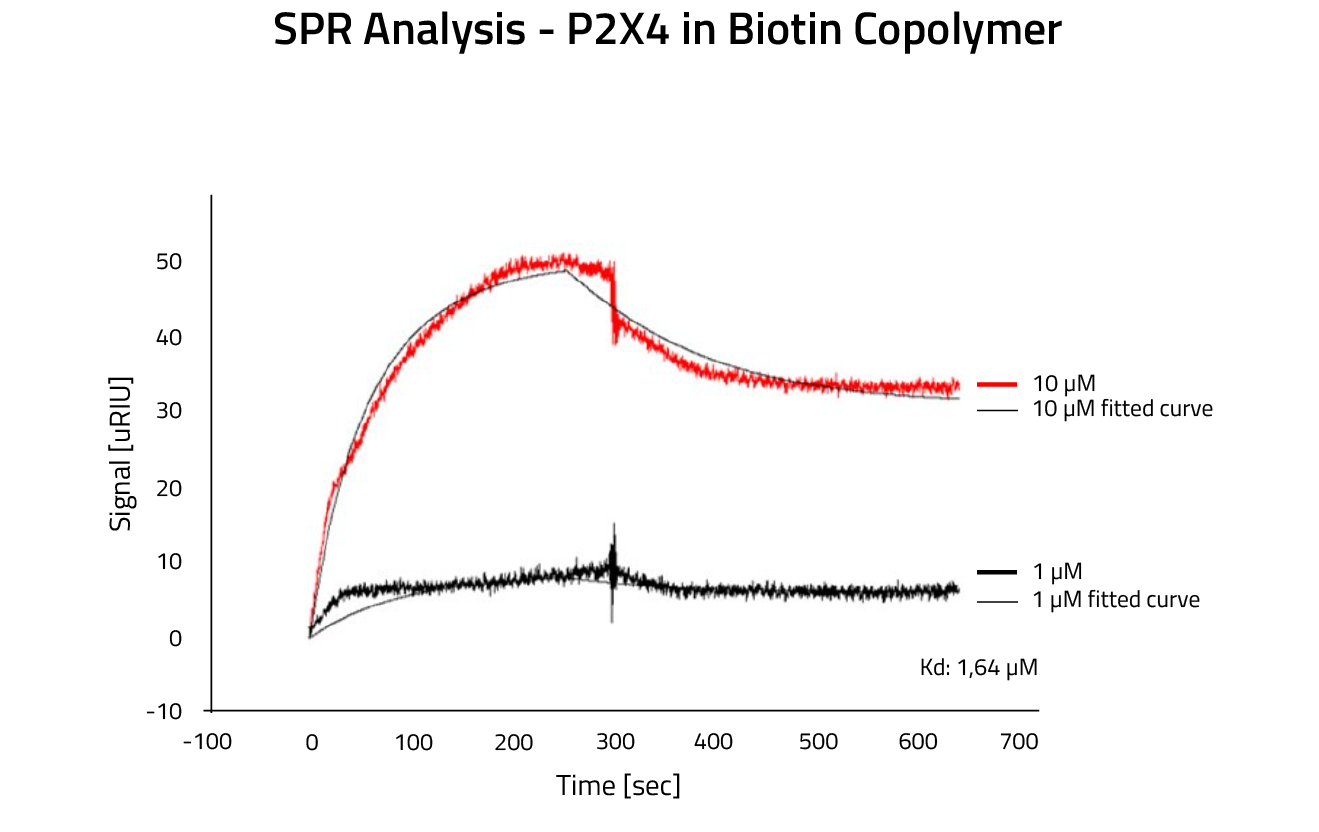
Lab Results
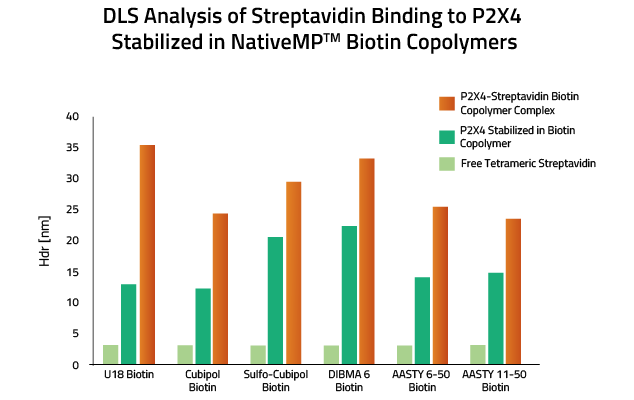
Disclaimer
Our products are intended for molecular biology applications. These products are not intended for the
diagnosis, prevention, or treatment of a disease.