SMALP BZ35
Order number: 18631
Description
The SMALP BZ series was developed in collaboration with Prof. Bert Klumperman from Nanosene, a spinout company of Stellenbosch University in South Africa. The goal was to create SMALPs that are synthesized via RAFT polymerization, achieving a better defined polymer size and a low dispersity (narrow chain length distribution). This is a significant improvement over previous SMALPs. The SMALP BZs are thus more efficient in dissolving the cell membranes and increasing protein yield.
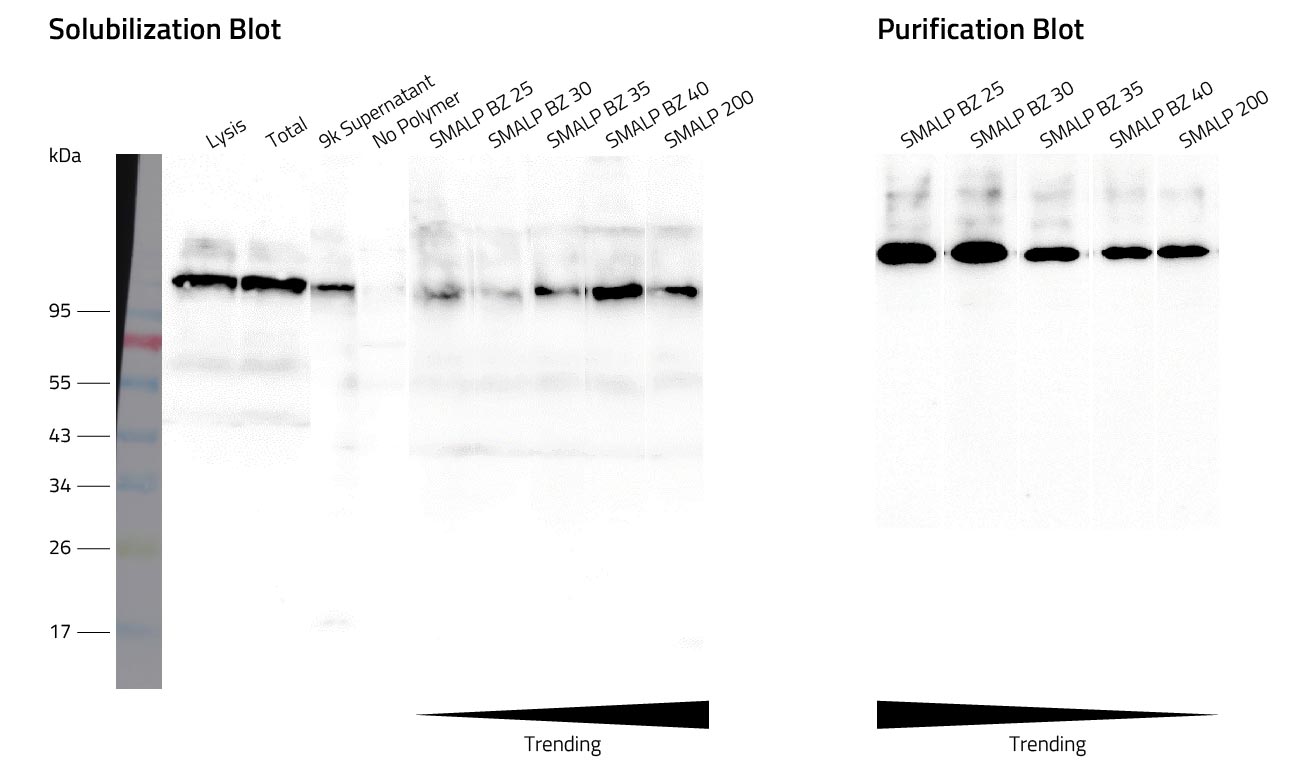
After successful solubilization of the membrane protein, the protein can be purified using affinity chromatography. For membrane protein purification we recommend using the Rho1D4-tag. Cube Biotech offers matching products for this purpose.
After successful solubilization of the membrane protein, the protein can be purified using affinity chromatography. For membrane protein purification we recommend using the Rho1D4-tag. Cube Biotech offers matching products for this purpose.
| Features | |
|---|---|
| Usage | Membrane protein solubilization & stabilization |
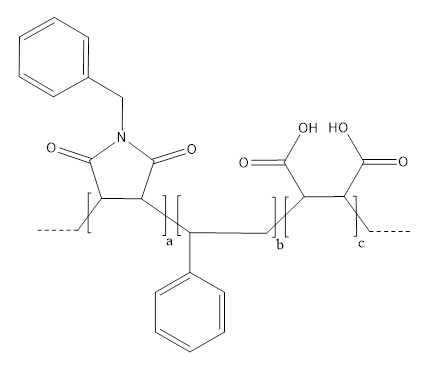
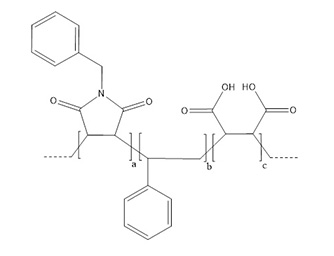
| Full-Name | Poly(styrene-co-maleic acid-co-35%(N-benzyl)maleimide) copolymer, sodium salt in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.5 |
| Formula Weight | 5,500 g/mol |
| Buffer | 50 mM HEPES |
| pH | 7.5 |
| State | Lyophilized Powder |
| Recommended concentration range upon use | 1% to 5% |
| Solubility | > 10 % in H2O |
| Color | White to slightly yellow |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Shipping Temperature | ambient temperature |
| Long-term Storage (lyophilized copolymer) | -20°C for several years |
| Short-term Storage (dissolved copolymer) | 2-8°C for several days |
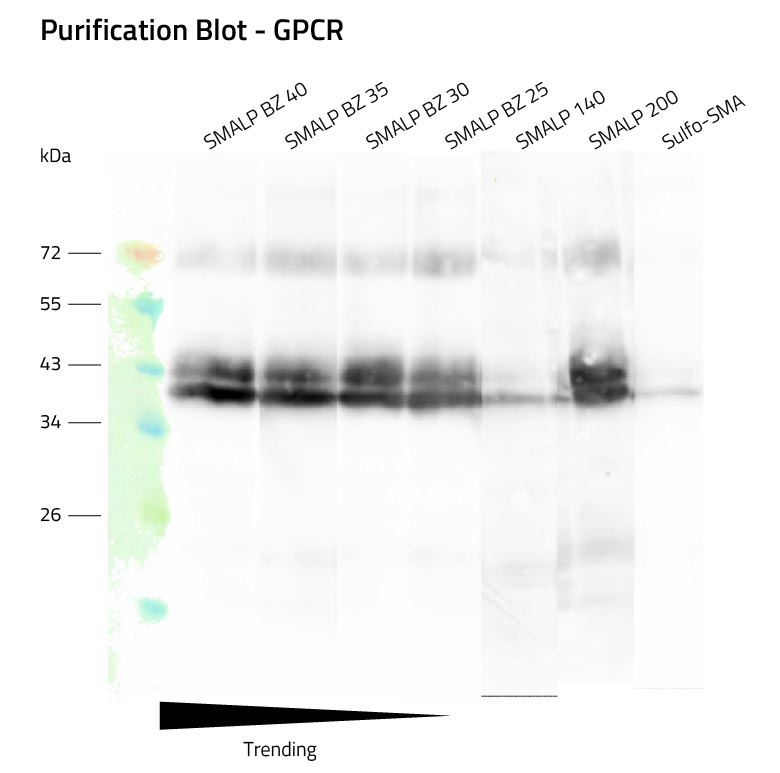
Lab Results
Video
Watch our video on the use of synthetic polymers for membrane protein solubilization. It demonstrates the use with SMALP.
FAQ
Can I have the datasheet for SMALP BZ35
Is SMALP BZ35 from Cube Biotech ready to use?
Yes, our SMALP BZ35 is ready to use. You can start directly with the solubilization. Read our protocol for more information.
Which pH is suitable for SMALP BZ35?
For SMALP BZ35 a pH of 7.5 is recommended.
Which concentrations of SMALP BZ35 should I use for my protein?
In general, we advise you to add 2,5 % SMALP BZ35 to your solution. But the optimal conditions have to be screened by yourself. In general you should not go below 1% or over 5%. Please refer to our Membrane Protein Solubilization Protocol for more information. Or simply ask our support team.
Disclaimer
Patent Pending
The purchaser is licensed under those patents to use the SMALP BZ35; for the manufacture of lipid particles and to use SMALP BZ35 so manufactured for the purpose of research and development of proteins, including their production (including purification and solubilization), screening, testing, analysis, characterization (including structural analysis and characterization), including for the purpose of drug screening, but not for the purpose of delivery of agents to humans or other animals for therapeutic, diagnostic, prophylactic purposes, which uses are specifically prohibited.
The purchaser is licensed under those patents to use the SMALP BZ35; for the manufacture of lipid particles and to use SMALP BZ35 so manufactured for the purpose of research and development of proteins, including their production (including purification and solubilization), screening, testing, analysis, characterization (including structural analysis and characterization), including for the purpose of drug screening, but not for the purpose of delivery of agents to humans or other animals for therapeutic, diagnostic, prophylactic purposes, which uses are specifically prohibited.