HisCube - Ni-INDIGO His-Tag Protein Purification MINI Kit
Order number: 80101
Description
The HisCube His-tag protein purification MINI Kit is our way to supply your laboratory with a convenient method for high-quality small-scale His-tag protein purifications. We put all of our experience in His-tag purifications into this Kit to provide a protocol that is easy to follow.
The HisCube Ni-INDIGO MINI Kit contains our in-house developed PureCube 100 Ni-INDIGO agarose resin and our PureCube 1-Step Batch MINI batch spin tubes.
INDIGO's greatest advantage is its tolerance towards reducing and chelating agents. These can be used to great help in His-tag purifications, but traditional His-tag affinity beads do not tolerate them. EDTA is a chelator that is often used in eukaryotic cell buffers because it has protease-inhibiting functions. DTT can dissolve protein aggregates that could potentially hinder the access of the purification beads to the His-tagged proteins. But thanks to INDIGO both substances can be used now. Therefore they are included in the Kit.
The HisCube Ni-INDIGO MINI Kit contains our in-house developed PureCube 100 Ni-INDIGO agarose resin and our PureCube 1-Step Batch MINI batch spin tubes.
INDIGO's greatest advantage is its tolerance towards reducing and chelating agents. These can be used to great help in His-tag purifications, but traditional His-tag affinity beads do not tolerate them. EDTA is a chelator that is often used in eukaryotic cell buffers because it has protease-inhibiting functions. DTT can dissolve protein aggregates that could potentially hinder the access of the purification beads to the His-tagged proteins. But thanks to INDIGO both substances can be used now. Therefore they are included in the Kit.
| Contents of the Kit |
|---|
| 2 x 50 ml Binding Buffer |
| 2 x 50 ml Wash Buffer |
| 1 x 50 ml Elution Buffer |
| 1 x 10 ml Ni-INDIGO resin |
| 50 x MINI Batch Spin Tubes |
| 50 x Collection Tubes |
| 1 x 500 mM DTT (add 1,016 mL ddH2O) |
| 1 x 500 mM EDTA (add 0.866 mL ddH2O) |
| Print-out of the protocol |
| Print-out of the fast protocol |
| Feature - Ni-INDIGO resin | |
|---|---|
| Usage | Specific binding and purification of 6x His tagged proteins |
| Specificity | Affinity to His-tagged proteins |
| Binding capacity | >100 mg/mL |
| Bead Ligand | Ni-INDIGO |
| Bead size | 100 μm |
| Filling quantity | Delivered as a 50 % suspension |
| pH stability | 2-14 |
| Chelator stability (e.g. EDTA) | 20mM |
| Reducing agent stability (e.g. DTT) | 20mM |
| Other stabilities | 100% methanol, 100% ethanol, 8 M urea, 6 M guanidinium hydrochloride, 30% (v/v) acetonitrile |
| Feature - PureCube MINI Batch Spin Column | |
|---|---|
| Body material | Polypropylene |
| Filter pore size | 0.1-0.2 µm low binding PVDF |
| Max. volume | 600 µl |
| Max. g force | 12,000-14,000 x g (45-degree fixed angle rotor) |
| Min. g force | 2,500 x g for 1 min |
Lab Results
INDIGO's key features
INDIGO was developed to solve two problems when it comes to His-tag protein purifications:
The chelator ligand that is mostly responsible for the tolerances against chemicals, capacity and purity. Therefore the goal was to develop & introduce a ligand that withstands commonly used reagents like EDTA, DTT and phenanthroline to give the user a huge benefit.
INDIGO was developed to solve two problems when it comes to His-tag protein purifications:
- The tolerance to certain cell buffer ingredients
- The comparatively low purity of His-tag purifications in general
The chelator ligand that is mostly responsible for the tolerances against chemicals, capacity and purity. Therefore the goal was to develop & introduce a ligand that withstands commonly used reagents like EDTA, DTT and phenanthroline to give the user a huge benefit.
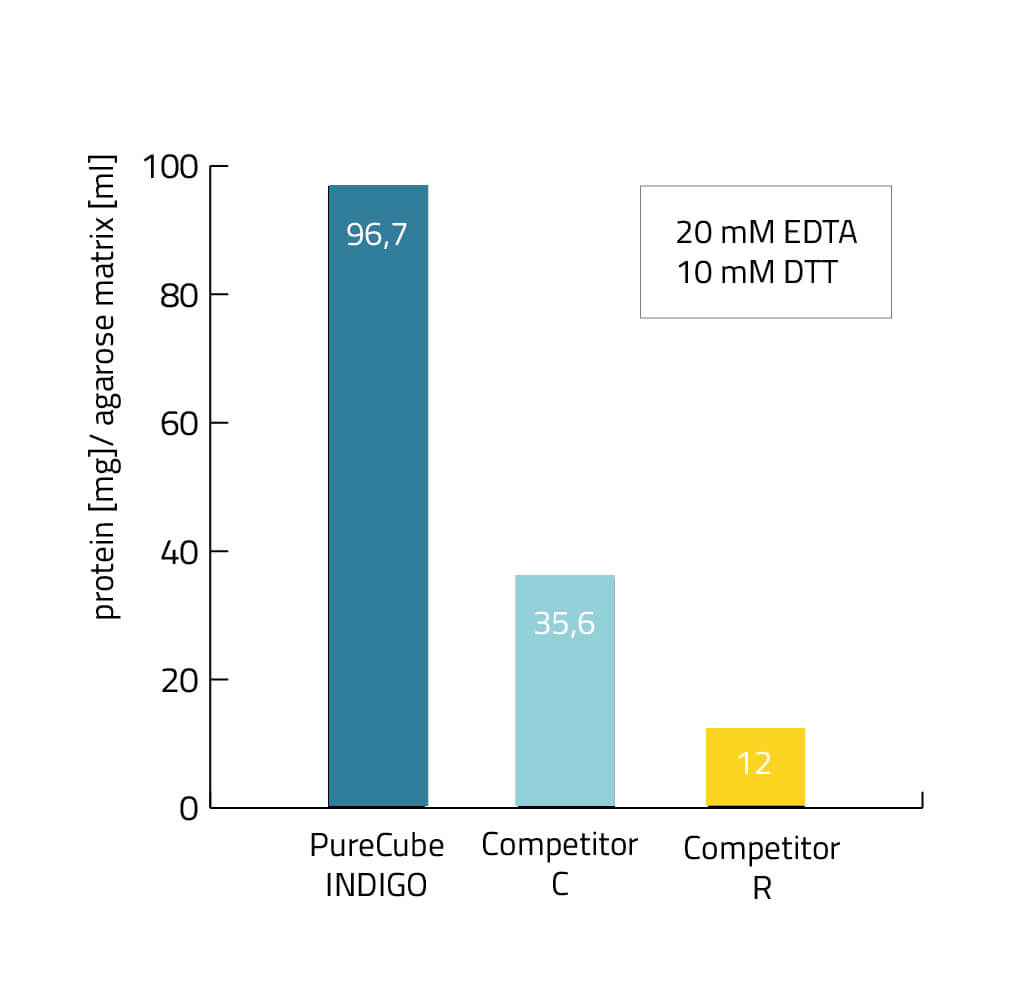
EDTA and DTT resistance of the INDIGO ligand
Protein purification is not limited to simple organisms like E.coli. Also more complex cells like mammalian cells or insect cell lines can be used to express & purify proteins. These systems come with more complex buffer compositions and some of their ingredients may interfere with traditional IMAC ligands. These include:
EDTA is often used in mammalian cell buffers to inhibit any proteases that would decrease the protein yield. But it also strips the NTA and IDA ligands of their nickel ions, thus making the beads useless.
DTT on the other hand can be used to dissolve protein aggregates in the cell lysate that might hinder the access to the protein's His-tag. By reducing nickel, thus making the beads useless.
Phenanthroline as a protease inhbitor is a strong chelator. And therefore behaves similar to EDTA.
To address all these issues, our R&D Team developed our INDIGO ligand that increases to EDTA, DTT and phenanthroline tolerance of a His-tag purification procedure up to 20 mM each.
Protein purification is not limited to simple organisms like E.coli. Also more complex cells like mammalian cells or insect cell lines can be used to express & purify proteins. These systems come with more complex buffer compositions and some of their ingredients may interfere with traditional IMAC ligands. These include:
EDTA is often used in mammalian cell buffers to inhibit any proteases that would decrease the protein yield. But it also strips the NTA and IDA ligands of their nickel ions, thus making the beads useless.
DTT on the other hand can be used to dissolve protein aggregates in the cell lysate that might hinder the access to the protein's His-tag. By reducing nickel, thus making the beads useless.
Phenanthroline as a protease inhbitor is a strong chelator. And therefore behaves similar to EDTA.
To address all these issues, our R&D Team developed our INDIGO ligand that increases to EDTA, DTT and phenanthroline tolerance of a His-tag purification procedure up to 20 mM each.
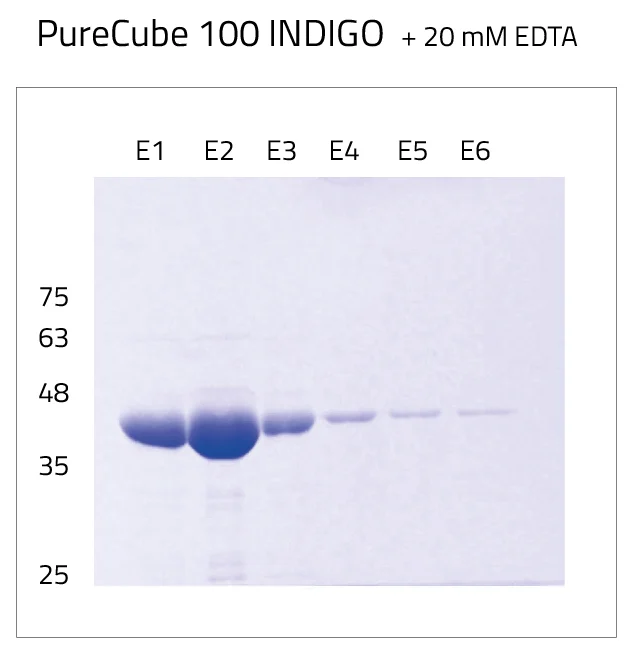
INDIGO's protein purity compared to Ni-NTA & reuseability
As previously mentioned, His-tag protein purification assays can fall behind in terms of purity compared to other affinity tags. Good examples for this are antibody-affinity tags like FLAG or Rho1D4.
On the other hand, FLAG and Rho1D4 purifications, result in very low protein amounts (up to 3-4 mg/ml resin at best) and are better suited for proteins with low abundance.
As previously mentioned, His-tag protein purification assays can fall behind in terms of purity compared to other affinity tags. Good examples for this are antibody-affinity tags like FLAG or Rho1D4.
On the other hand, FLAG and Rho1D4 purifications, result in very low protein amounts (up to 3-4 mg/ml resin at best) and are better suited for proteins with low abundance.

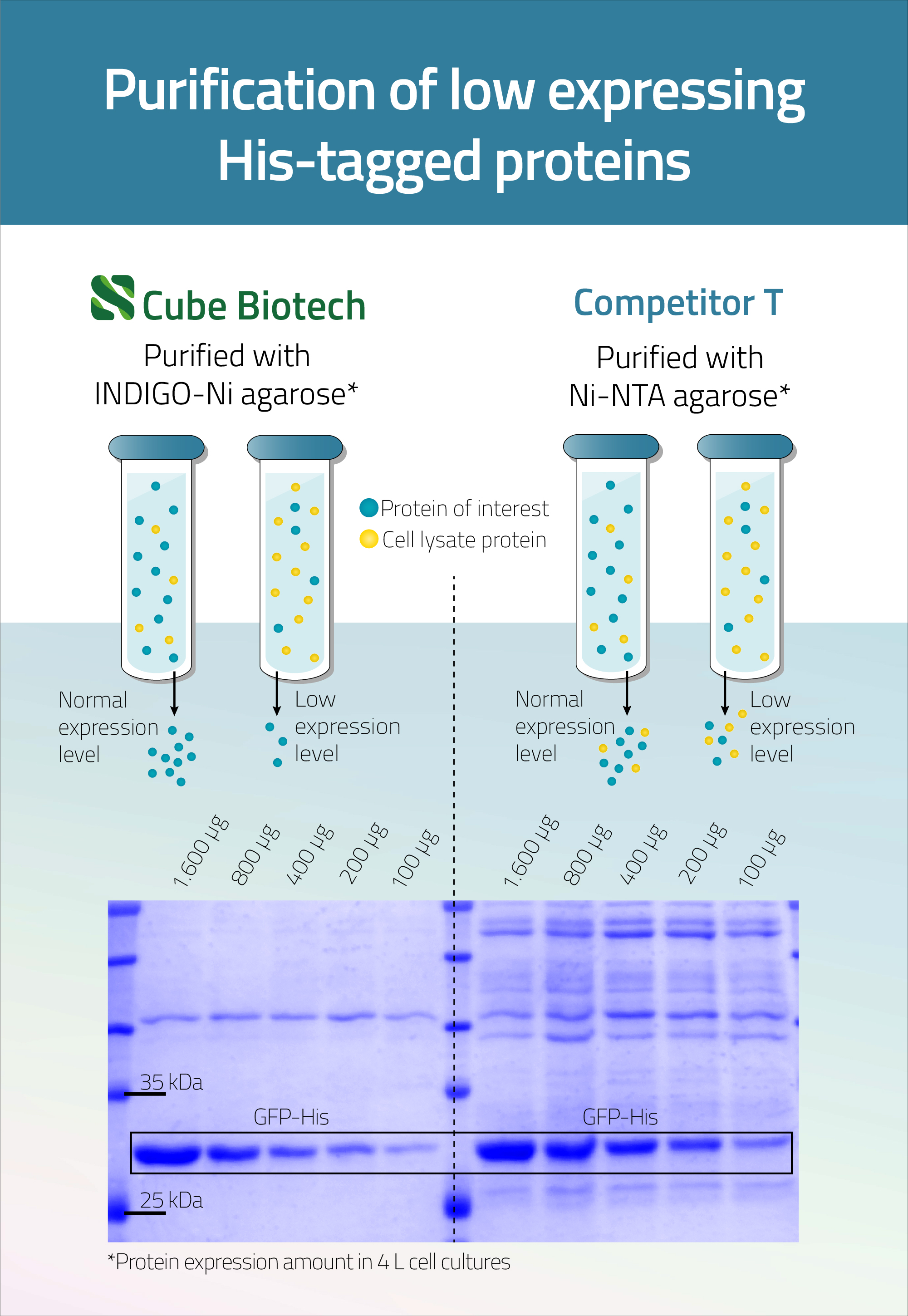
His-tag protein purification achieves the highest possible protein yields. In our in-house quality controls for Ni-INDIGO resin we usually get around 100 mg protein per ml resin. The protein used for the quality controls is His-tagged GFP. This Video-Guide shows His-Tag purification using our His-Affinity beads.
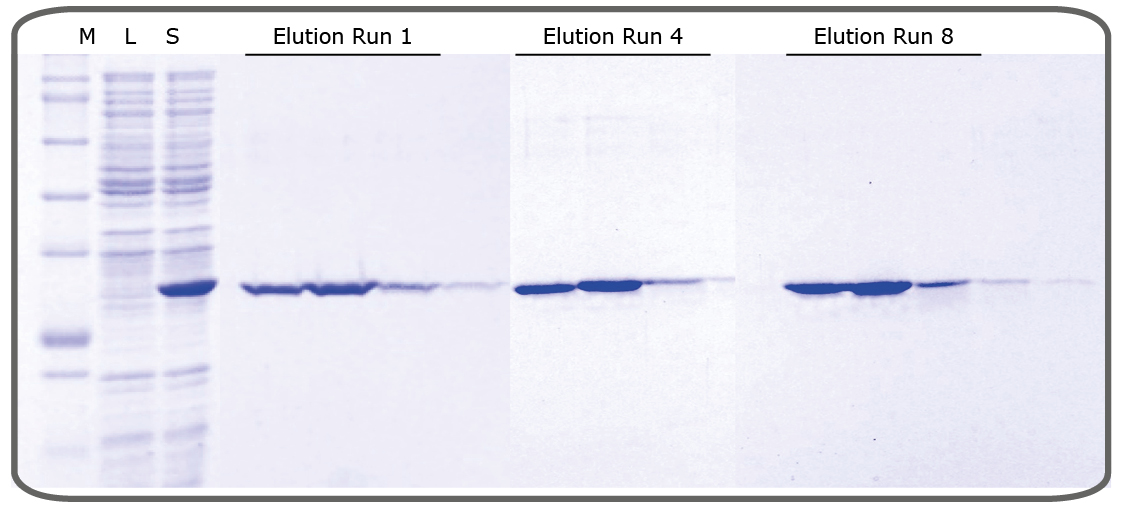
Furthermore, INDIGO beads can be reused multiple times as demonstrated in figure 3. In addition to that they can be regenerated following this protocol.
Video
Video Guide - Batch Spin Chromatography
FAQ
Can I get the protocol and/or datasheet for the HisCube Ni-INDIGO MINI Kit?
What are the reasons for nonspecific binding?
Some histidine-rich proteins can also bind to nickel. But washing with NaOH after elution of your protein of interest removes unspecific bound proteins from your resin.
Why should I add EDTA to my His-tag purification buffers?
EDTA is a chelator, meaning it binds cations. Cations are common Co-factors for proteases. The addition of EDTA, therefore, ensures that proteases that may still be present in your solutions, become inactive.
Why should I add DTT to my His-tag purification buffers?
DTT is a reducing agent. Its purpose is to mimic the natural reducing tendency of the cytosol. With it, proteins can aggregate through the formation of new, unwanted disulfide bridges. DTT prevents this from happening.
I ran out of one of the chemicals or materials of the HisCube MINI Kit. Can I order it separately?
Of course, you can! Here is the list of chemicals/materials that you can order on their own.
Can Ni-INDIGO beads be stripped like NTA or IDA beads?
No, this is not possible.
Can I reuse Ni-INDIGO beads or can I regenerate them?
Yes, you can reuse the beads! We recommend using our INDIGO washing & regeneration protocol at least after every 5th use of the beads.




