Synthetic Nanodisc Screening Kit MAXI (23x2x50 mg)
Order number: 18295
Description




The versatility of membrane proteins and their composition mirrors the intricate nature of the cell membrane. As a result, it can be a challenge to predict with absolute certainty the optimal copolymer for the solubilization and subsequent stabilization of your membrane protein of interest.
Therefore, we have combined our most prominent SMALP, DIBMA, AASTY, and Amphipol products into this practical synthetic copolymer nanodisc Screening Set MAXI to help you find the correct product.
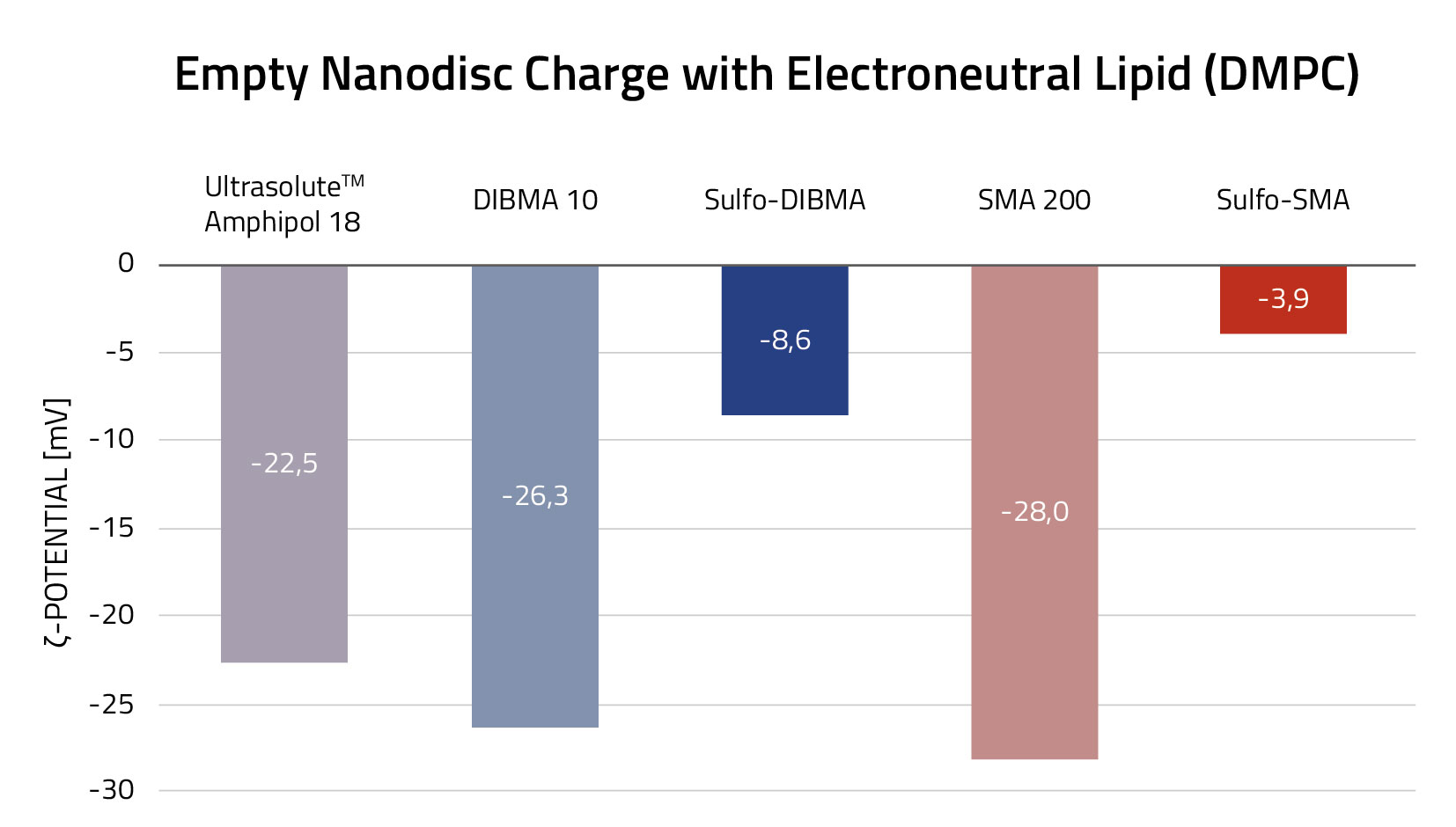
All 23 products are buffered in HEPES to provide maximal comparability between the individual screening assays. In the product description, you can find the complete list of copolymers included in this kit and their specific features.
For general features applicable to all copolymers see Table 1. For more specific features of the individual copolymers see Tables 2 – 6.
Update May 2024: Access the protocol based on the Masterclass by MIT‘s Greg Dodge (PhD): Copolymer Purification Protocol for Screening Approach.
All 23 products are buffered in HEPES to provide maximal comparability between the individual screening assays. In the product description, you can find the complete list of copolymers included in this kit and their specific features.
For general features applicable to all copolymers see Table 1. For more specific features of the individual copolymers see Tables 2 – 6.
Update May 2024: Access the protocol based on the Masterclass by MIT‘s Greg Dodge (PhD): Copolymer Purification Protocol for Screening Approach.
Datasheets
- DIBMA 10 Datasheet
- DIBMA 12 Datasheet
- DIBMA Glucosamine Datasheet
- DIBMA Glycerol Datasheet
- Glyco-DIBMA Datasheet
- Sulfo-DIBMA Datasheet
- SMALP 140-I Datasheet
- SMALP 140 Datasheet
- SMALP 200 Datasheet
- SMALP 300 Datasheet
- SMALP BZ25 Datasheet
- SMALP BZ30 Datasheet
- SMALP BZ35 Datasheet
- SMALP BZ40 Datasheet
- Sulfo-SMA Datasheet
- AASTY 6-45 Datasheet
- AASTY 6-50 Datasheet
- AASTY 6-55 Datasheet
- AASTY 11-45 Datasheet
- AASTY 11-50 Datasheet
- AASTY 11-55 Datasheet
- Amphipol 17 Datasheet
- Amphipol 18 Datasheet
Table 1: Shared Features
This table lists the features that every of the 23 Copolymers share.
| Feature | |
|---|---|
| Use | Solubilization & stabilization of membrane proteins |
| Buffer | HEPES |
| pH (upon solving in dH2O) | 7.5 |
| State upon delivery | Lyophilized powder |
| Recommended concentration for use | 1% - 5% |
| Shipping Temperature | Room temperature |
| Long-term Storage (lyophilized copolymer) | -20°C for several years |
| Short-term Storage (dissolved copolymer) | 2°C - 8°C for several days |
Table 2: Included SMALP Products
| Feature | SMALP 140 | SMALP 140-I | SMALP 200 | SMALP 300 | Sulfo-SMA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 5 kDa | 5 kDa | 6.5 kDa | 10 kDa | 8 kDa |
| Polymerization Type | Free-Radical | Free-Radical | Free-Radical | Free-Radical | RAFT |
| Nanodisc Diameter | Diverse | Diverse | Diverse | Diverse | Uniform |
| Divalent cationic tolerance | < 5 mM | < 100 mM | < 5 mM | < 5 mM | > 100 mM |
| Absorption at 280nm | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Solulbility in dH2O | 45% | 38% | 40% | 35% | > 10 % |
Table 3: Included SMALP BZ Products
| Table 3: Feature | SMALP BZ25 | SMALP BZ30 | SMALP BZ35 | SMALP BZ40 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 5.5 kDa | 5.5 kDa | 5.5 kDa | 5.5 kDa |
| Polymerization Type | RAFT | RAFT | RAFT | RAFT |
| Nanodisc Diameter | Uniform | Uniform | Uniform | Uniform |
| Divalent cationic tolerance | < 5 mM | < 5 mM | < 5 mM | < 5 mM |
| Absorption at 280nm | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Solulbility in dH2O | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % |
Table 4: Included DIBMA Products
| Feature | DIBMA 10 | DIBMA 12 | DIBMA Glycerol | DIBMA Glucosamine | Glyco-DIBMA | Sulfo-DIBMA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 10 kDa | 12 kDa | 10 kDa | 10 kDa | 10 kDa | 15.7 kDa |
| Polymerization Type | Free-Radical | Free-Radical | Free-Radical | Free-Radical | Free-Radical | RAFT |
| Nanodisc Diameter | Diverse | Diverse | Diverse | Diverse | Diverse | Uniform |
| Divalent cationic tolerance | < 5 mM | < 5 mM | < 50 mM | < 50 mM | < 4 mM | > 100 mM |
| Absorption at 280nm | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Solulbility in dH2O | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % |
Table 5: Included AASTY Products
| Feature | AASTY 6-45 | AASTY 6-50 | AASTY 6-55 | AASTY 11-45 | AASTY 11-50 | AASTY 11-55 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 5-6 kDa | 5-6 kDa | 5-6 kDa | 10-11 kDa | 10-11 kDa | 10-11 kDa |
| Polymerization Type | RAFT | RAFT | RAFT | RAFT | RAFT | RAFT |
| Nanodisc Diameter | Uniform | Uniform | Uniform | Uniform | Uniform | Uniform |
| Divalent cationic tolerance | < 6 mM | < 6 mM | < 6 mM | < 6 mM | < 6 mM | < 6 mM |
| Absorption at 280nm | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Solulbility in dH2O | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % | > 10 % |
Table 6: Included Amphipol Products
| Feature | Ultrasolute™ Amphipol 17 | Ultrasolute™ Amphipol 18 |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | 7.3 kDa | 7.3 kDa |
| Polymerization Type | Free-Radical | Free-Radical |
| Nanodisc Diameter | Diverse | Diverse |
| Divalent cationic tolerance | < 10 mM | < 25 mM |
| Absorption at 280nm | No | No |
| Solulbility in dH2O | > 10 % | > 10 % |
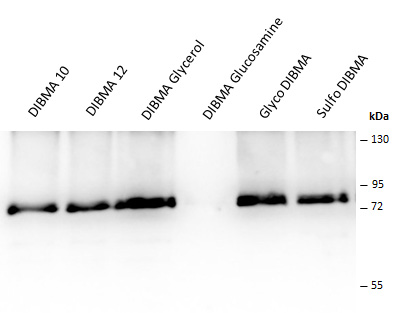
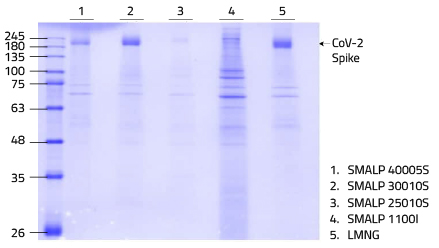
Lab Results
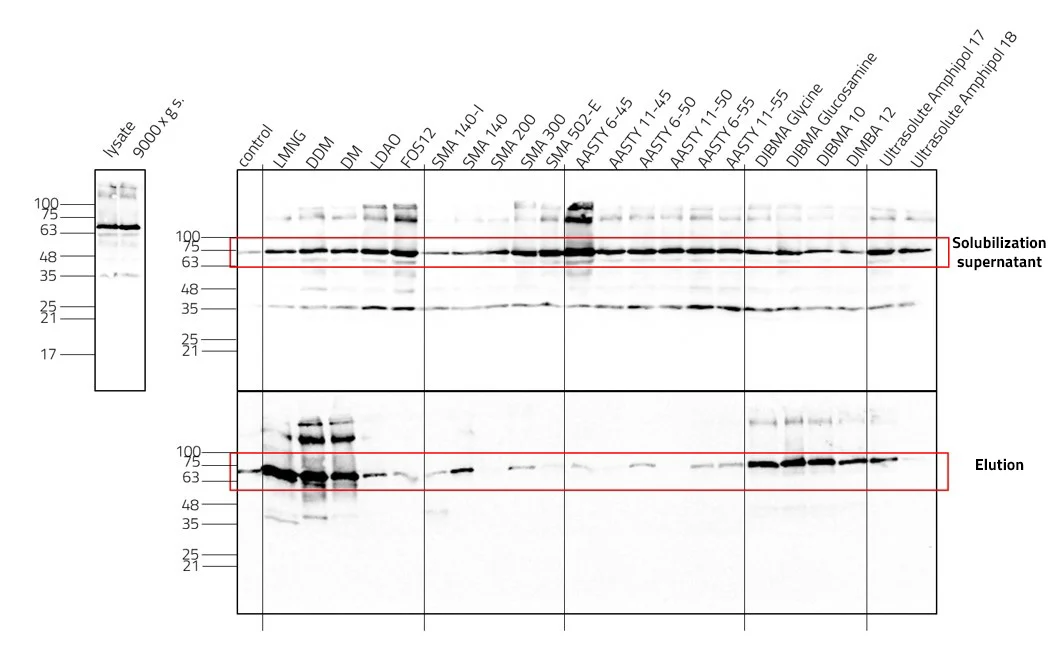
_Gelbild SMALP BZs.jpg)
Video
Watch our video on the use of Copolymers for membrane protein solubilization. It demonstrates the use with SMALP.
FAQ
Is DIBMA from Cube Biotech ready to use?
Yes, our DIBMA is ready to use. You can start directly with solubilization. Read our protocol for more information.
Which pH is suitable for DIBMA?
For DIBMA a pH of 7.5 is recommended. DIBMA does not solubilize if the pH is smaller than 6.5.
Which concentrations of DIBMA should I use for my protein?
In general, we advise you to add 2,5 % DIBMA to your solution. But the optimal conditions have to be screened by yourself.
I used DIBMA for protein solubilization and a white precipitate appeared - what happened?
Your DIBMA precipitated. You should check your pH and ensure that your pH never drops down to 6.5.
What SMA is the best one to use?
This is a tricky question, as it depends on the membrane protein which SMA performs best, however, SMA 200 is in general the most recommended. Keep in mind that this is no guarantee for it to be the best but in our experience, it is a good allrounder.
What are the recommended concentrations of SMA?
Mix the supplied solutions at a concentration of 1-5% SMALP to the total solution. These conditions can be used as indications. The optimal SMA concentration must be determined separately for each experiment.
How is SMA stored?
Store in cool and dry places, protected from direct sunlight. Long-term storage is recommended at 4°C
The viscosity of my SMA has decreased, what happene
This can occur by storing SMA at low temperatures (as recommended!). Simply warm the SMA solution up to room temperature to restore its original viscosity.
How do I quantify the amount of protein after SMA treatment?
In contrast to DIBMA, SMA absorbs light at 280 nm similar to proteins. Therefore ultraviolet absorption is no option here. However other protein quantification assays are viable options like:
- Bicinchoninic Acid (BCA)
- Bradford
- Folin-Lowry in some cases
Disclaimer
The use of this styrene maleic acid copolymer (SMA) product for the manufacture of styrene maleic acid copolymer - lipid particles (SMALP), and the use of SMALP, are covered by one or more of the following patents owned by Malvern Cosmeceutics Limited: US 8623414, EP 1890675, GB 2426703, AU 2006253886, JP 5142898, IN 261468, CN ZL200680018957.2 and CA 2,611,144 and by the University of Birmingham: US 8754168.
The purchaser is licensed under those patents to use the SMA for the manufacture of SMALP and to use the SMALP for the purpose of research and development of proteins, including their production (including purification and solubilisation), screening testing, analysis, characterisation (including structural analysis and characterisation), including for the purpose of drug screening and for the purpose of in vitro diagnostics, but not for the purpose of delivery of agents to humans or other animals for therapeutic, diagnostic (including in vivo diagnostics) or prophylactic purposes, which uses are specifically prohibited.
The purchaser is licensed under those patents to use the SMA for the manufacture of SMALP and to use the SMALP for the purpose of research and development of proteins, including their production (including purification and solubilisation), screening testing, analysis, characterisation (including structural analysis and characterisation), including for the purpose of drug screening and for the purpose of in vitro diagnostics, but not for the purpose of delivery of agents to humans or other animals for therapeutic, diagnostic (including in vivo diagnostics) or prophylactic purposes, which uses are specifically prohibited.
Patent Pending
The purchaser is licensed under those patents to use the SMALP BZ; for the manufacture of lipid particles and to use SMALP BZ so manufactured for the purpose of research and development of proteins, including their production (including purification and solubilization), screening, testing, analysis, characterization (including structural analysis and characterization), including for the purpose of drug screening, but not for the purpose of delivery of agents to humans or other animals for therapeutic, diagnostic, prophylactic purposes, which uses are specifically prohibited.
The purchaser is licensed under those patents to use the SMALP BZ; for the manufacture of lipid particles and to use SMALP BZ so manufactured for the purpose of research and development of proteins, including their production (including purification and solubilization), screening, testing, analysis, characterization (including structural analysis and characterization), including for the purpose of drug screening, but not for the purpose of delivery of agents to humans or other animals for therapeutic, diagnostic, prophylactic purposes, which uses are specifically prohibited.